Making CAPTCHAs that beat ChatGPT
Using Stable Diffusion and ControlNet to create a new CAPTCHA design that is human readable, but not AI readable.
CAPTCHAs
aka Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart
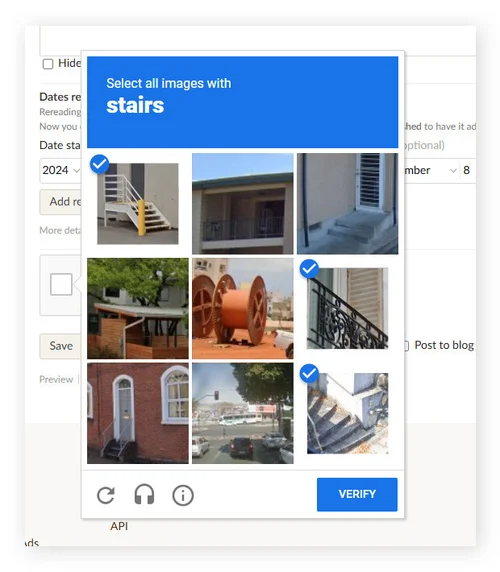
If you’ve spent any time online, you’ll probably be very familiar with one of these:
These puzzles help keep the internet ‘secure’ by distinguishing humans from bots. However, recent advancements in AI have made these kinds of CAPTCHAs basically meaningless, with studies showing that AI can solve them 100% of the time. At the same time, humans often struggle with these challenges, resulting in over half of internet traffic now coming from these bots.
And so it begs the question: “can we use the AI to beat the AI?”
The Problem with Traditional CAPTCHAs
At their core, AI models are great at recognizing complex patterns, which is why they can easily bypass traditional CAPTCHAs. These puzzles rely on visual or textual challenges that optical character recognition (OCR) and other AI technologies (like vision-enabled LLMs) can decode. To counter this, we need a new approach-one that can trick AI and humans alike.
Enter Stable Diffusion and ControlNet
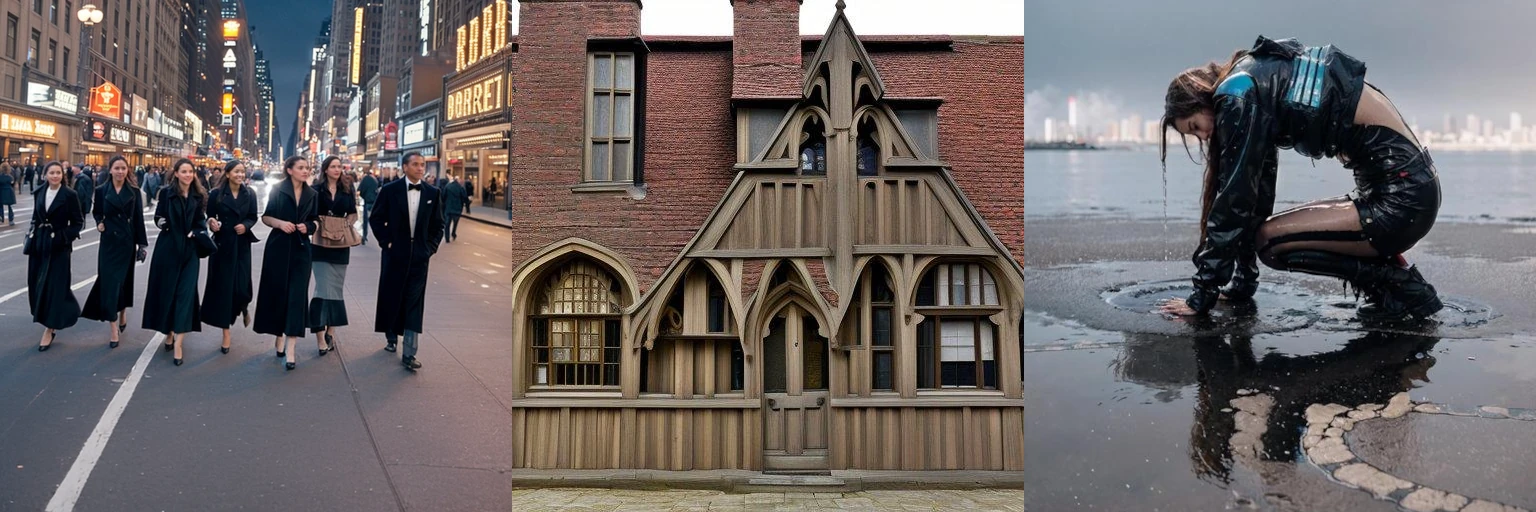
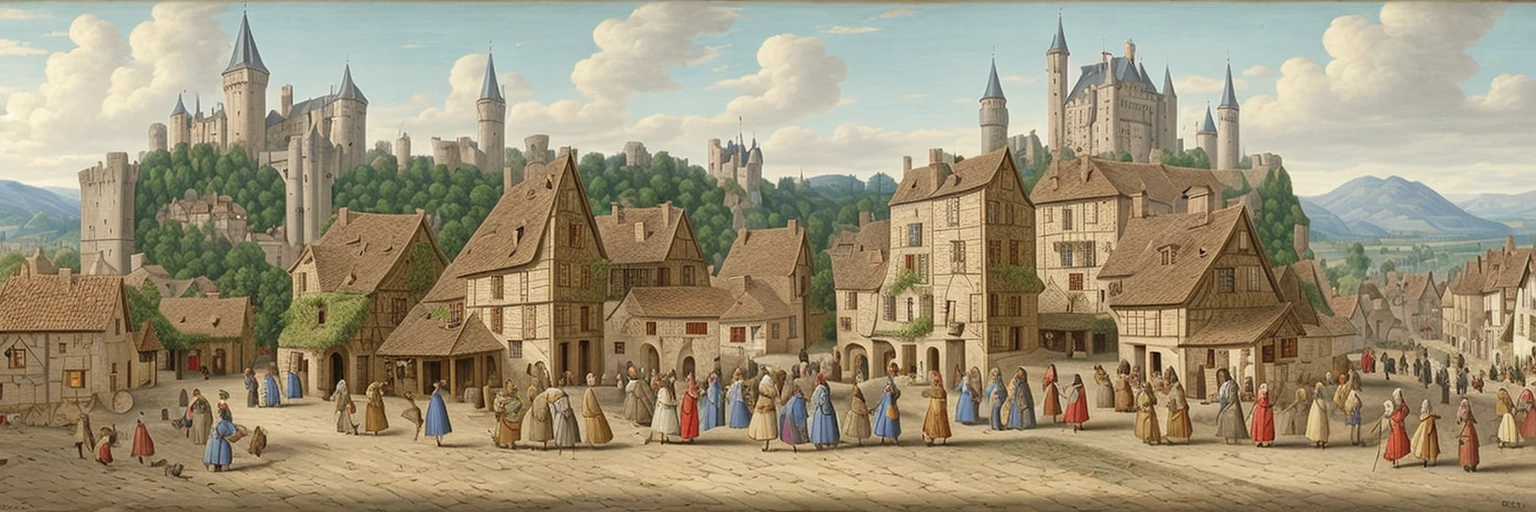
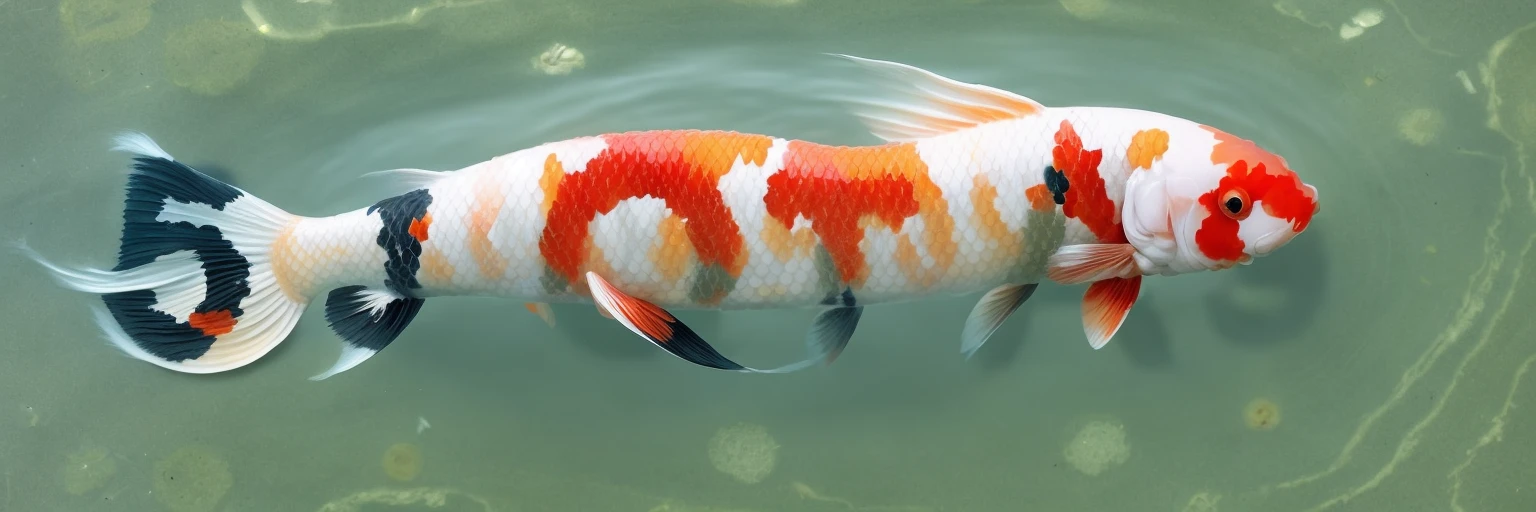
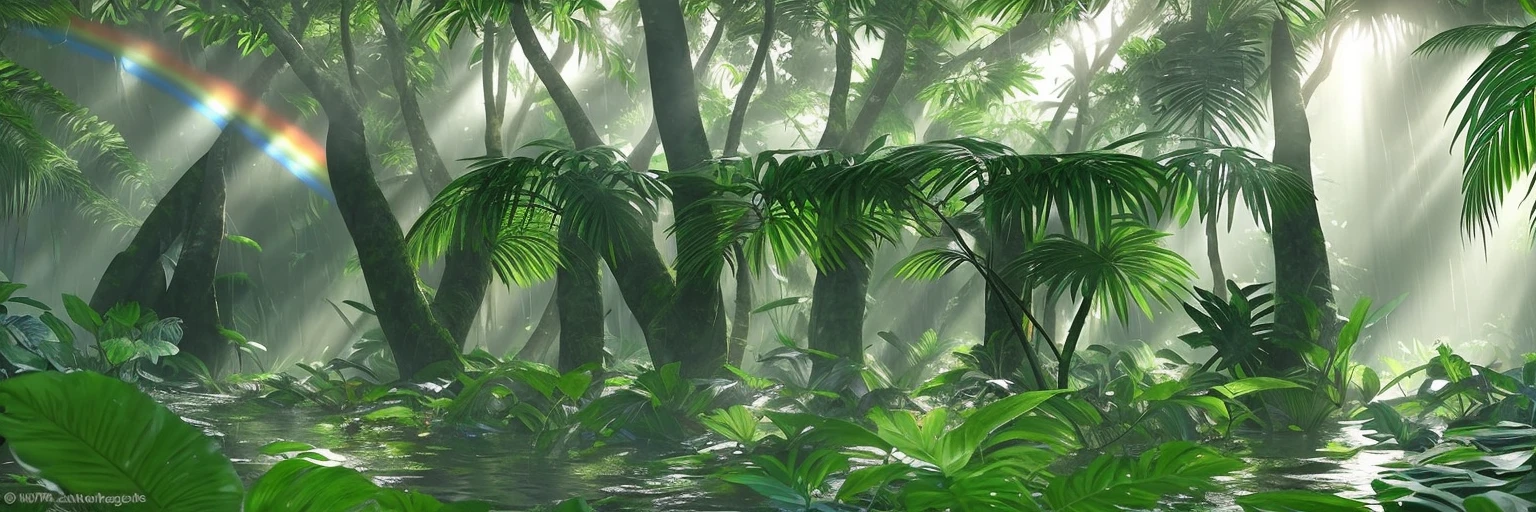
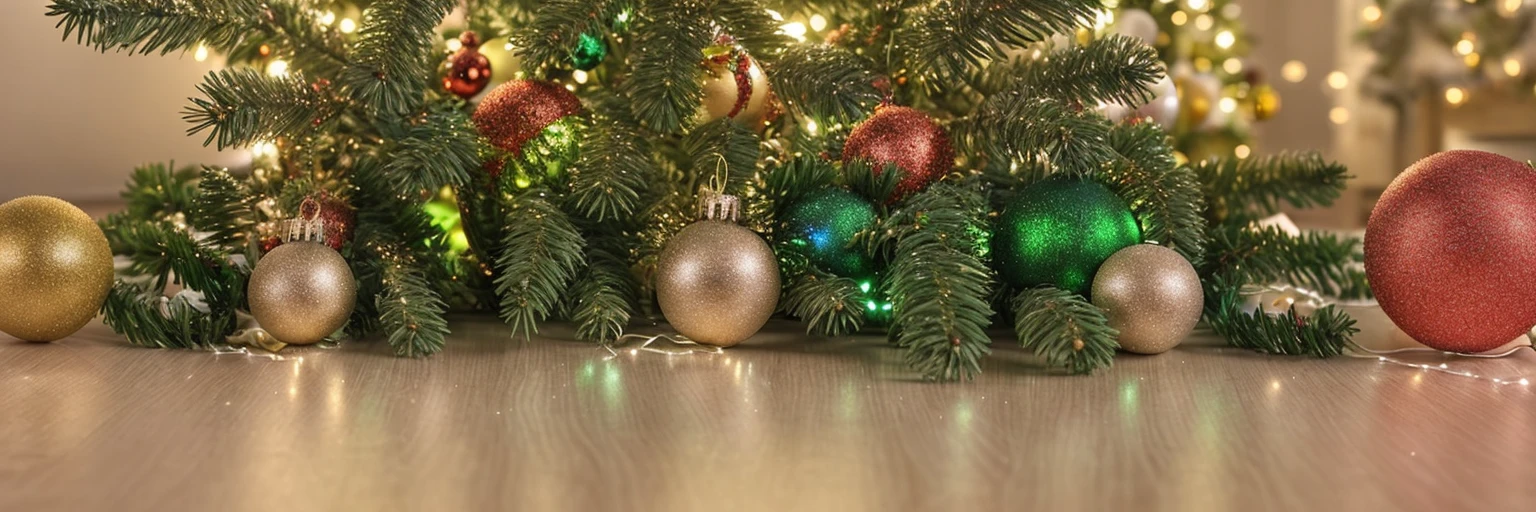
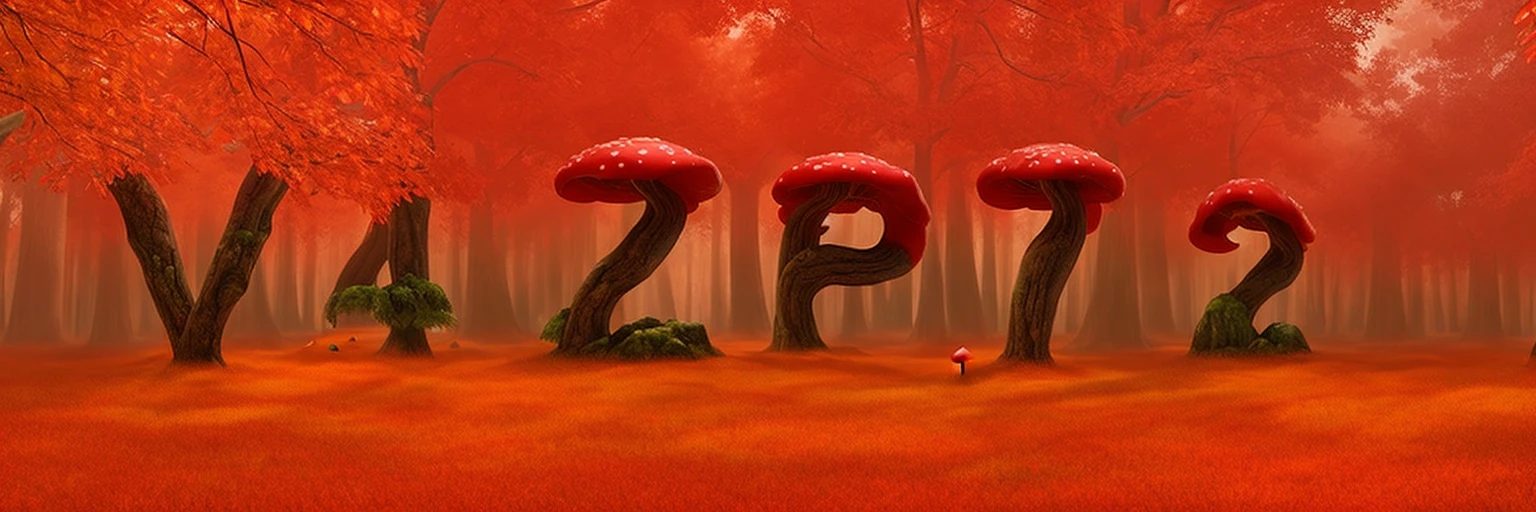
Controlnet is a seperate “attachment” to stable diffusion models, which allows for additional inputs to guide the diffusion process towards a certain goal. In the original paper, it was mainly used for generic structural guidance. However, it’s popularity really blew up when people realised it can be used to create qr codes that look like ‘normal’ images but are in-fact fully functional. With the help of additional techniques, this process was perfected, and resulted in some popular memes:
This can actually help solve a lot of problems that are currently faced with todays’ captchas, which have to carefully balance readability with simulated complexity; the same task that OCR tech is great at defeating. Instead, we can use controlnet to hide the text in normal looking images.
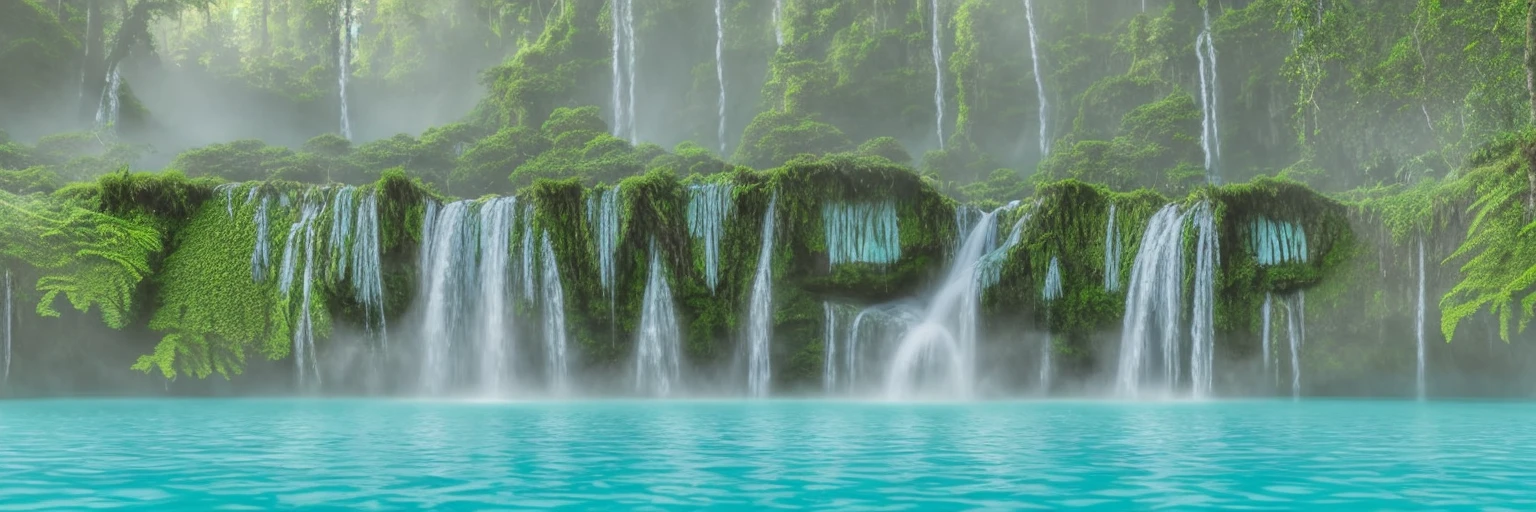
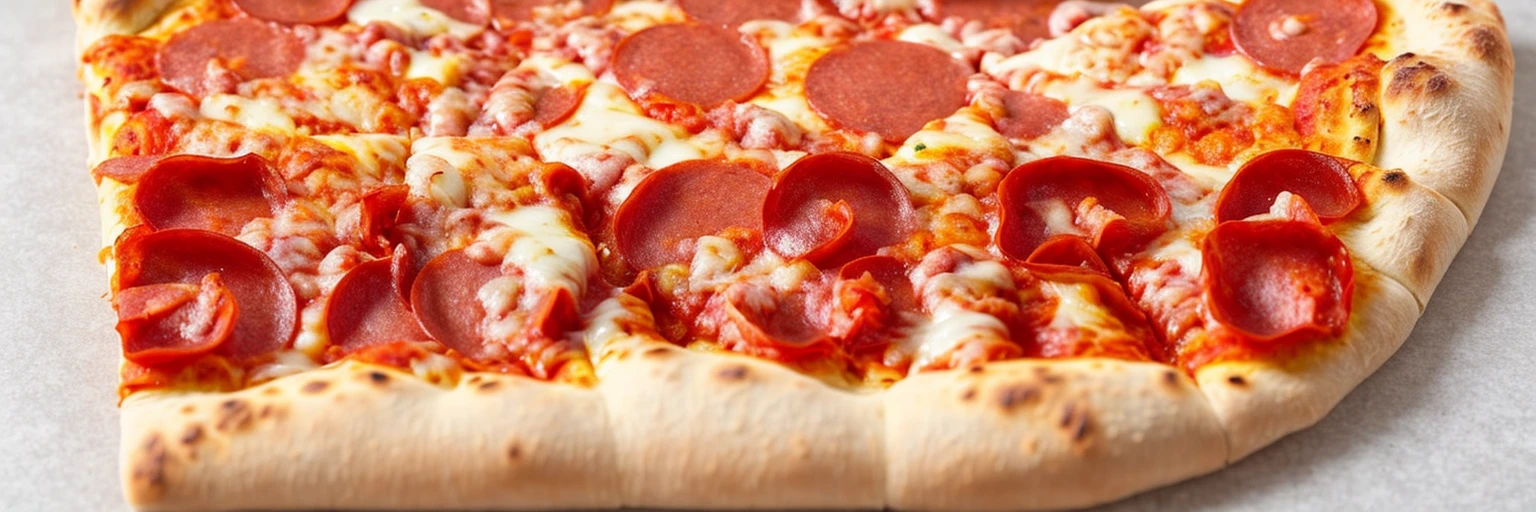
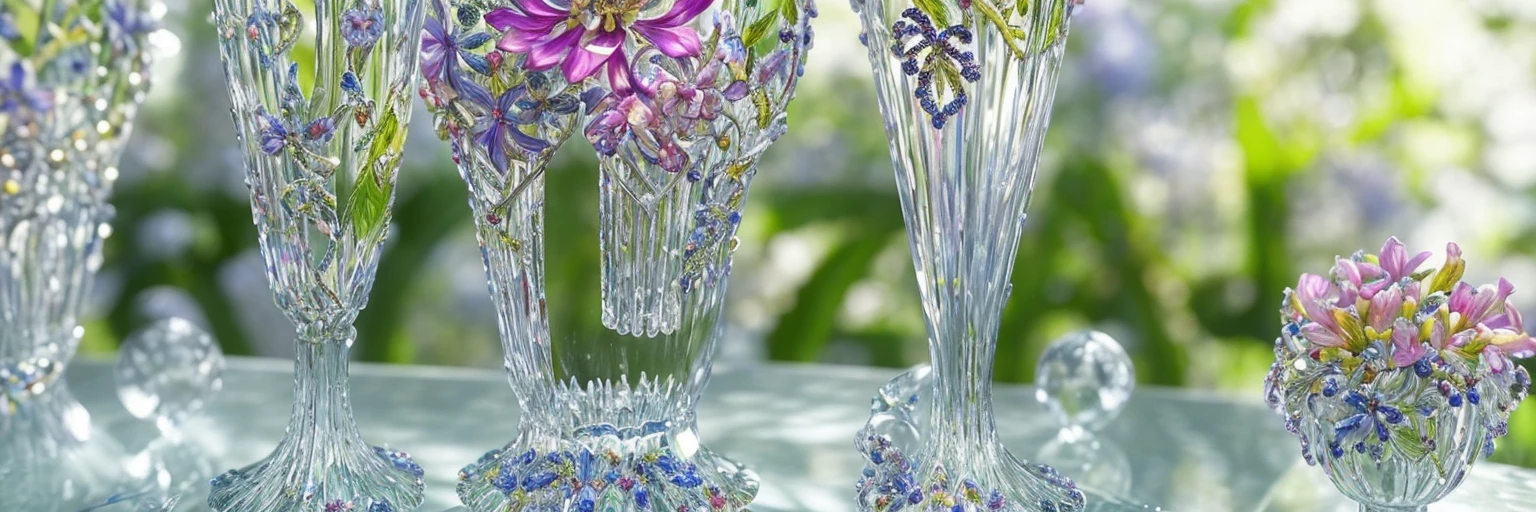
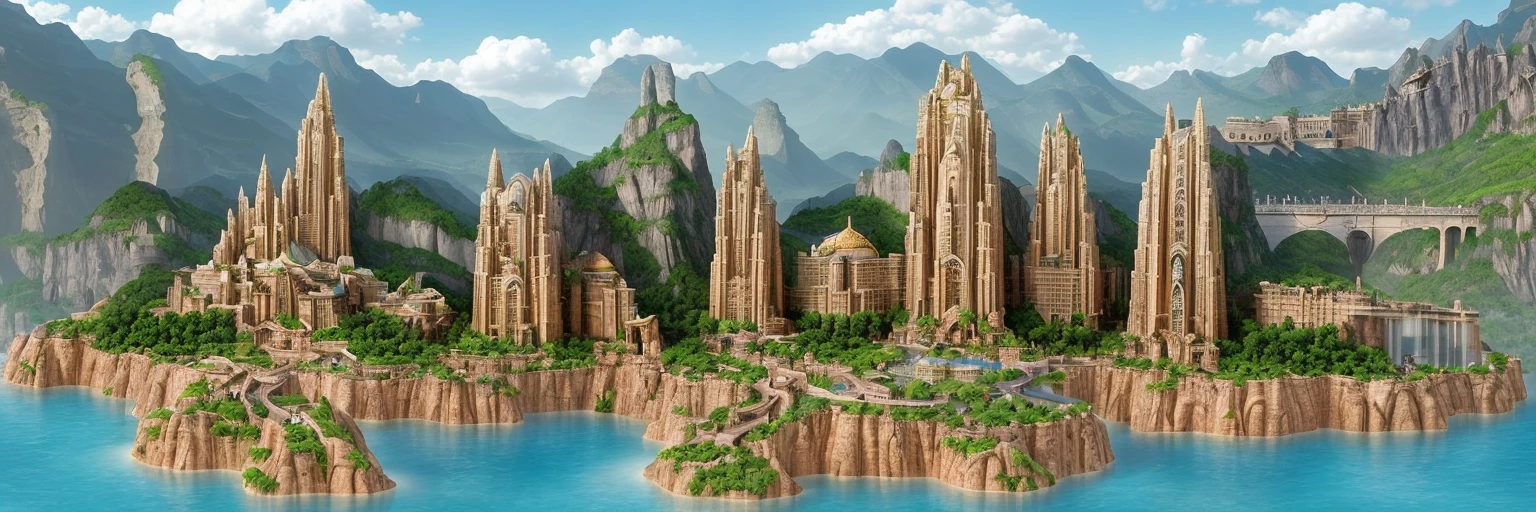
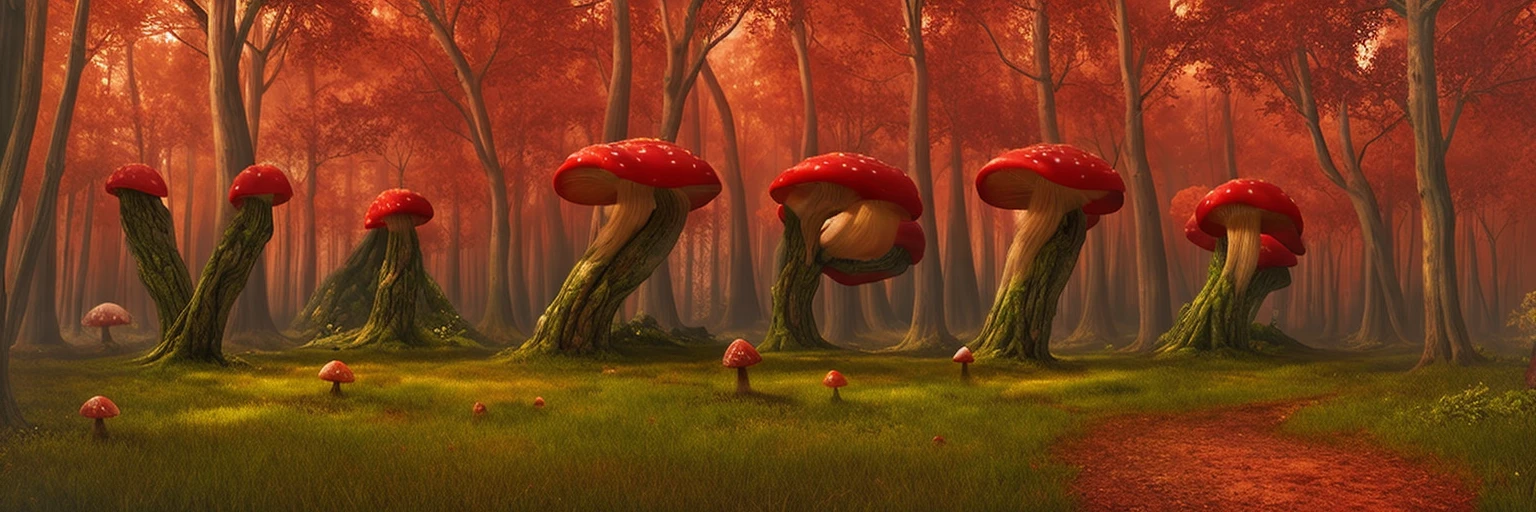
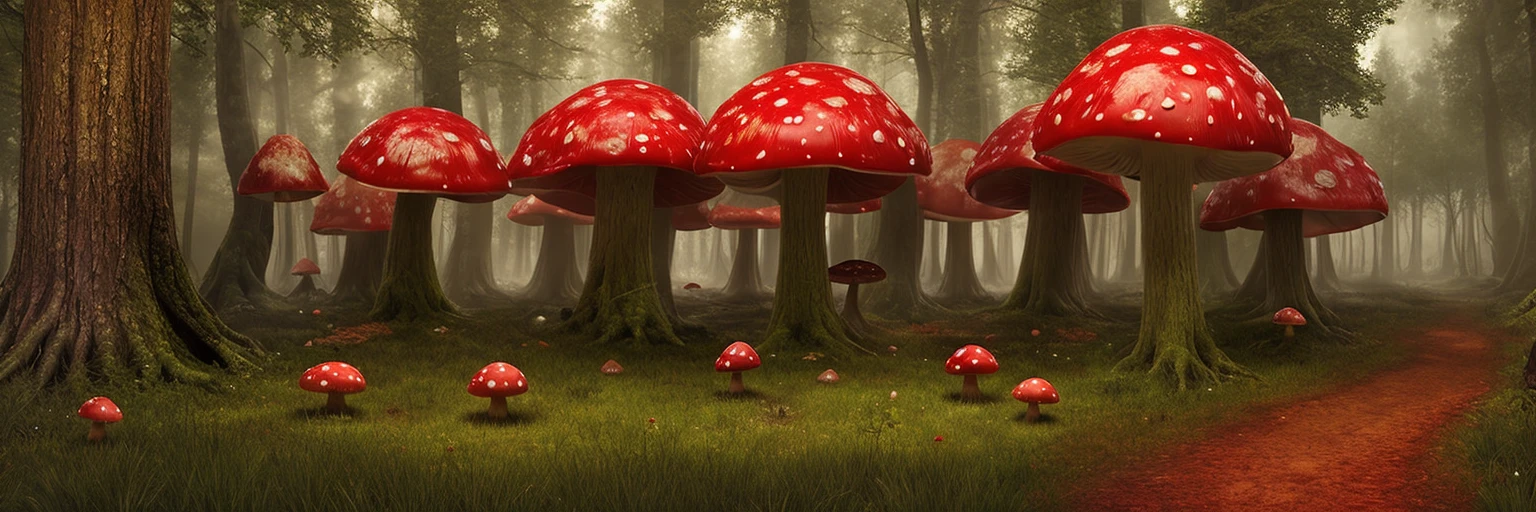
By generating a captcha mask, then combining it with a randomly generated prompt, we can develop some interesting results:
Why It Works So Well
If you’ve never experienced the results of controlnet, then it might take a second to ‘read between the lines’ and realise that there are two images in one. However, because we humans are pretty good at learning on the spot, it becomes trivial to solve these kinds of CAPTCHAs once you’re used to them. This is also exactly why LLMs (like Grok, ChatGPT, and Gemini) struggle with them; they’ve never been trained on them!
Customizability and Difficulty Levels
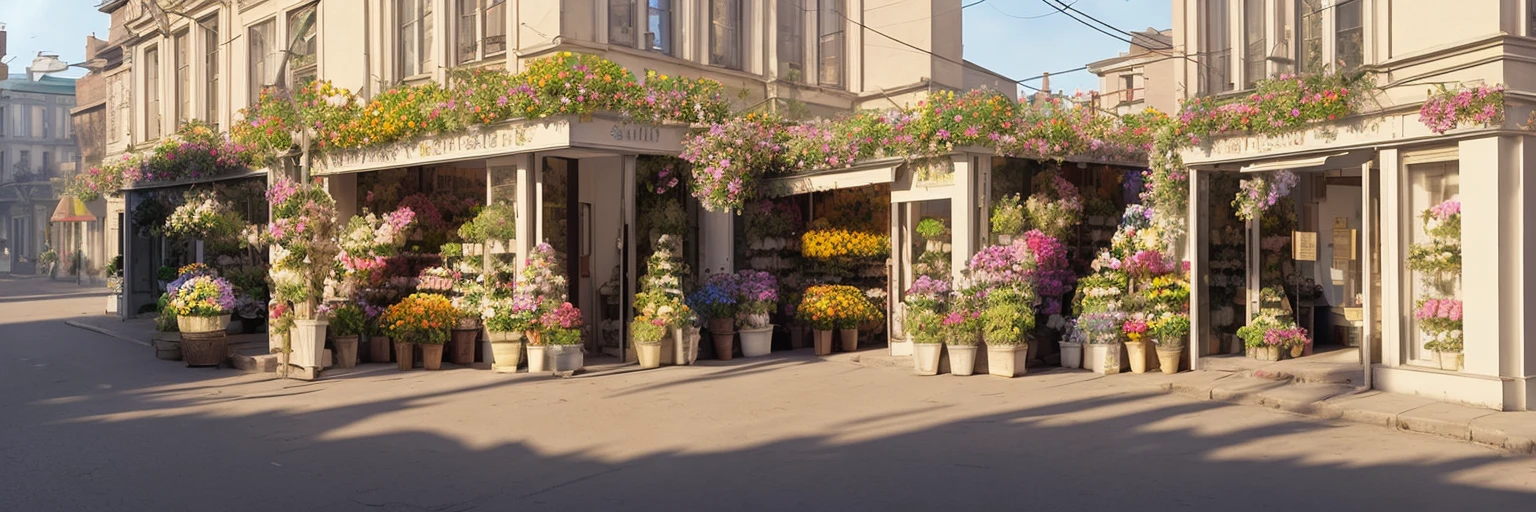
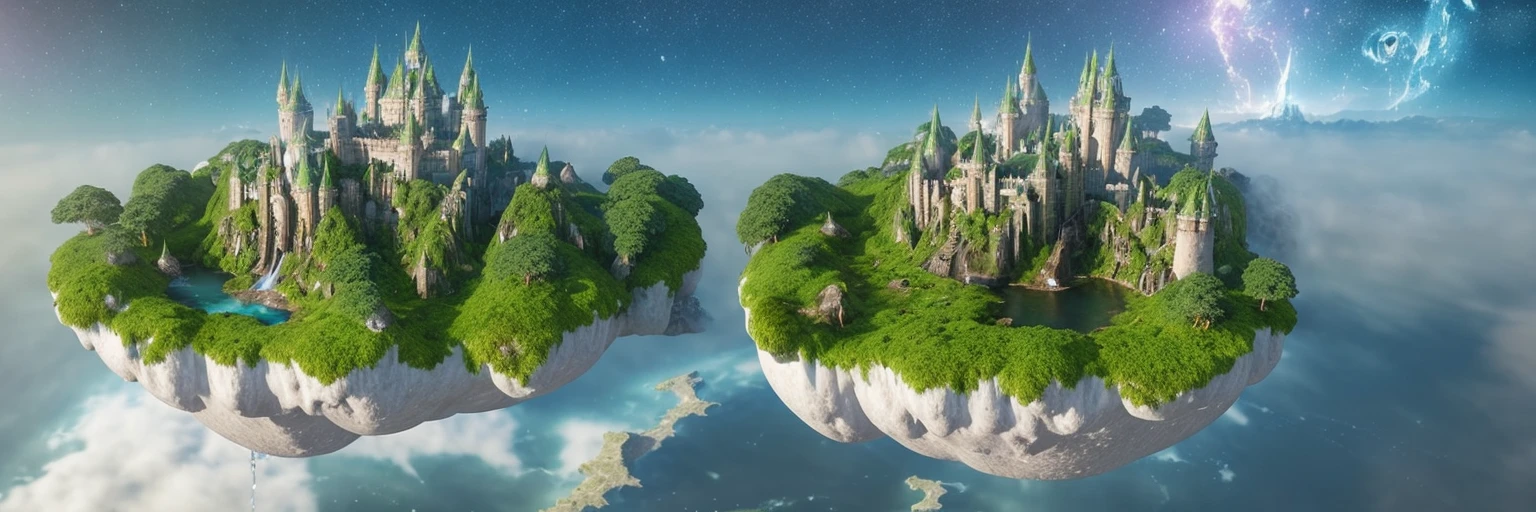
But that’s not all - because we can modify the ‘strength’ of controlnet, we can also create CAPTCHAs that range from ‘easy’ to ‘hard’:
Advantages Over Traditional CAPTCHAs
- AI Resistance: The complex patterns generated by ControlNet are difficult for AI to decode, unlike traditional CAPTCHAs that rely on distorted text or simple images.
- Human-Friendly: Humans can still read the embedded text with relative ease, reducing frustration.
- Infinite Variability: Random prompts and masks ensure a vast array of unique CAPTCHAs, making it harder for bots to train on specific patterns.
- Scalability: ControlNet’s integration with Stable Diffusion allows for rapid generation of new CAPTCHA designs.
Challenges and Future Directions
As AI continues to evolve, new models may eventually crack these kinds of CAPTCHAs, especially if they become popular, or if a big tech firm feels like training a multi-billion parameter model for this one task. Despite this, for the time being, this is probably one of a handful of unbeatable CAPTCHA designs in this current AI cycle.
Conclusion
By using Stable Diffusion and ControlNet to create next-generation CAPTCHAs, we can beat current gen LLMs without making it impossible for humans to pass the challenge. As AI advances, leveraging AI to fight AI may just be the key to securing the web.